| SPARK-GAP VOLTAGES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Based
on results of the American Institute of Electric Engineers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Air at 760 mmHg,
25 C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Peak
Voltage |
Needle points |
Diameter
of spherical electrodes, [cm] |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
2,5 |
5 |
10 |
25 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| [kV] |
[cm] |
[cm] |
[cm] |
[cm] |
[cm] |
|
| 5 |
0,42 |
0,13 |
0,15 |
0,15 |
0,16 |
|
| 10 |
0,85 |
0,27 |
0,29 |
0,30 |
0,32 |
|
| 15 |
1,30 |
0,42 |
0,44 |
0,46 |
0,48 |
|
| 20 |
1,75 |
0,58 |
0,60 |
0,62 |
0,64 |
|
| 25 |
2,20 |
0,76 |
0,77 |
0,78 |
0,81 |
|
| 30 |
2,69 |
0,95 |
0,94 |
0,95 |
0,98 |
|
| 35 |
3,20 |
1,17 |
1,12 |
1,12 |
1,15 |
|
| 40 |
3,81 |
1,41 |
1,30 |
1,29 |
1,32 |
|
| 45 |
4,49 |
1,68 |
1,50 |
1,47 |
1,49 |
|
| 50 |
5,20 |
2,00 |
1,71 |
1,65 |
1,66 |
|
| 60 |
6,81 |
2,82 |
2,17 |
2,02 |
2,01 |
|
| 70 |
8,81 |
4,05 |
2,68 |
2,42 |
2,37 |
|
| 80 |
11,10 |
|
3,26 |
2,84 |
2,74 |
|
| 90 |
13,30 |
|
3,94 |
3,28 |
3,11 |
|
| 100 |
15,50 |
|
4,77 |
3,75 |
3,49 |
|
| 110 |
17,70 |
|
5,79 |
4,25 |
3,88 |
|
| 120 |
19,80 |
|
7,07 |
4,78 |
4,28 |
|
| 130 |
22,00 |
|
|
5,35 |
4,69 |
|
| 140 |
24,10 |
|
|
5,97 |
5,10 |
|
| 150 |
26,10 |
|
|
6,64 |
5,52 |
|
| 160 |
28,10 |
|
|
7,37 |
5,95 |
|
| 170 |
30,10 |
|
|
8,16 |
6,39 |
|
| 180 |
32,00 |
|
|
9,03 |
6,84 |
|
| 190 |
33,90 |
|
|
10,00 |
7,30 |
|
| 200 |
35,70 |
|
|
11,10 |
7,76 |
|
| 210 |
37,60 |
|
|
12,30 |
8,24 |
|
| 220 |
39,50 |
|
|
13,70 |
8,73 |
|
| 230 |
41,40 |
|
|
15,30 |
9,24 |
|
| 240 |
43,30 |
|
|
|
9,76 |
|
|
|
| 250 |
45,20 |
|
|
|
10,30 |
|
| 300 |
54,70 |
|
|
|
13,30 |
|
|
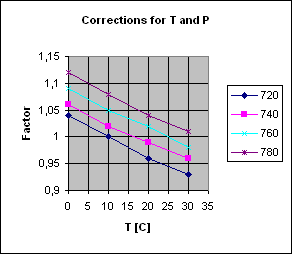
| CORRECTIONS
FOR TEMPERATURE AND PRESSURE |
|
| Values
found in the above table may be corrected for temperature and pressure |
|
| by
multiplying the values given by the appropriate correction factor found
below: |
|
| Pressure [mmHg] |
|
| Temp. [C] |
720 |
740 |
760 |
780 |
|
| 0 |
1,04 |
1,06 |
1,09 |
1,12 |
|
kV |
cm |
|
| 10 |
1 |
1,02 |
1,05 |
1,08 |
|
20 |
1,75 |
|
| 20 |
0,96 |
0,99 |
1,02 |
1,04 |
|
22,78 |
2 |
Interpolation |
|
| 30 |
0,93 |
0,96 |
0,98 |
1,01 |
|
25 |
2,2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
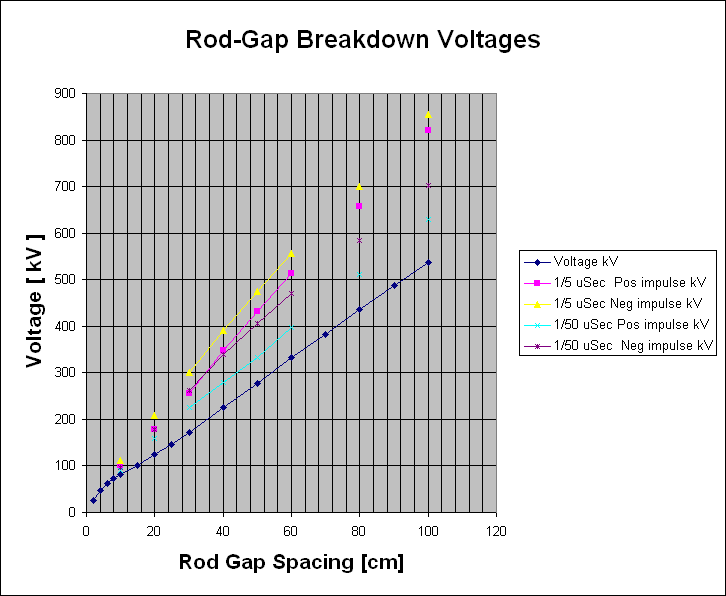
| Rod Gap Breakdown Voltage
Tables |
|
|
| More
details on Rod Gap procedures and construction |
|
|
| The
following table values valid for: |
|
|
| 1.27 cm square rods |
|
| 27 deg C |
|
| 760 torr (1013 mBar) |
|
| 15.5 torr water vapor pressure |
|
| (11 g/cc water content for impulses). |
|
|
| The voltages in the table reflect the
breakdown of the rod gap +/- 8% |
|
|
| Rod Gap |
Voltage |
1/5 uSec |
1/5 uSec |
1/50 uSec |
1/50 uSec |
|
| Spacing |
|
Pos impulse |
Neg
impulse |
Pos
impulse |
Neg impulse |
|
| cm |
kV |
kV |
kV |
kV |
kV |
|
| 2 |
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 4 |
47 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 6 |
62 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 8 |
72 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 10 |
81 |
101 |
111 |
90 |
97 |
|
| 15 |
102 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 20 |
124 |
179 |
208 |
160 |
178 |
|
| 25 |
147 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 30 |
172 |
256 |
301 |
226 |
262 |
|
| 40 |
225 |
348 |
392 |
279 |
339 |
|
| 50 |
278 |
431 |
475 |
334 |
407 |
|
| 60 |
332 |
513 |
557 |
397 |
470 |
|
| 70 |
382 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 80 |
435 |
657 |
701 |
511 |
585 |
|
| 90 |
488 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 100 |
537 |
820 |
855 |
629 |
703 |
|
|
| Humidity
Correction |
|
|
| H20 Vapor Press. (torr) |
2,5 |
5 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
25 |
30 |
|
| Correction Factor % |
-16,5 |
-13,1 |
-6,5 |
-0,5 |
4,4 |
7,9 |
10,1 |
|
|
| Data taken
from tables and graphs in Naidu & Kamaraju, High Voltage Engineering. |
|
|
| Copyright
1998, Jim Lux / rodv.htm / 5
May 1998 / |
|
|
| |
|
|
| Sphere
Gap Breakdown Voltage Tables |
|
|
| The
following two tables give the breakdown voltages for a standard |
|
| sphere gap
of the specified sphere size and spacing. The standard |
|
| accuracy is
±3% for gaps less than half the sphere diameter and 5% for |
|
| gaps larger
than that. The first table is for a gap with one terminal |
|
| grounded,
typically a vertical gap. There are two columns for each sphere |
|
| size
depending on whether it is a positive or negative impulse. The second |
|
| table is
for a gap with both terminals at HV. The values from these tables |
|
| will need
to be corrected for current atmospheric conditions, particularly |
|
| humidity. |
|
|
|
| Sphere gap with one terminal grounded |
|
|
| A -> AC, DC, either polarity and full negative standard
impulse voltages (one sphere grounded) |
|
| B -> positive polarity standard impulse voltages and impulse
voltages with long tails (either polarity) |
|
|
|
|
| |
Sphere Diameter (cm) |
|
| Gap Spacing |
5 |
10 |
15 |
25 |
50 |
100 |
150 |
200 |
|
| cm |
A |
B |
A |
B |
A |
B |
A |
B |
A |
B |
A |
B |
A |
B |
A |
B |
|
| 0,5 |
17,4 |
17,4 |
16,9 |
16,8 |
16,9 |
16,9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
32 |
32 |
31,7 |
31,7 |
31,4 |
31,4 |
31,2 |
31,4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1,5 |
44,7 |
45,5 |
44,7 |
45,1 |
44,7 |
45,1 |
44,7 |
44,7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
57,5 |
58 |
58 |
58 |
58 |
58 |
58 |
58 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2,5 |
|
|
71,5 |
71,5 |
71,5 |
71,5 |
71,5 |
71,5 |
71,5 |
71,5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 3 |
|
|
85 |
85 |
85 |
85 |
85 |
85 |
85 |
85 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 3,5 |
|
|
95,5 |
96 |
97 |
97 |
97 |
97 |
97 |
97 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 4 |
|
|
106 |
108 |
108 |
110 |
110 |
110 |
110 |
110 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 5 |
|
|
123 |
127 |
127 |
132 |
135 |
136 |
136 |
136 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 7,5 |
|
|
|
|
181 |
187 |
195 |
196 |
199 |
199 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
257 |
268 |
259 |
259 |
262 |
262 |
262 |
262 |
262 |
262 |
|
| 12,5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
277 |
294 |
315 |
317 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
309 |
331 |
367 |
974 |
383 |
384 |
384 |
384 |
384 |
384 |
|
| 17,5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
336 |
362 |
413 |
425 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
452 |
472 |
500 |
500 |
500 |
500 |
500 |
500 |
|
| 25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
520 |
545 |
605 |
610 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
575 |
610 |
700 |
715 |
730 |
735 |
735 |
740 |
|
| 35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
725 |
755 |
785 |
800 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
862 |
885 |
940 |
950 |
960 |
965 |
|
| 45 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
925 |
965 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1000 |
1020 |
1110 |
1130 |
1160 |
1170 |
|
| 75 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1210 |
1260 |
1420 |
1460 |
1510 |
1590 |
|
| 100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1870 |
1900 |
|
| |
|
|
| symmetrical
sphere gaps |
|
|
| 20deg C,
760 torr, either polarity impulse, AC, DC |
|
| spacings
<0.5D Accuracy +/- 3% ; spacings >=0.5D accuracy +/- 5% |
|
|
| |
Sphere
Diameter (cm) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| gap (cm) |
5 |
10 |
|
15 |
25 |
50 |
100 |
150 |
200 |
|
| 0,5 |
17,5 |
16,9 |
|
16,5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
32,2 |
31,6 |
|
31,3 |
31 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 1,5 |
46,1 |
45,8 |
|
45,5 |
45 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
58,3 |
59,3 |
|
59,2 |
59 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 2,5 |
69,4 |
72,4 |
|
72,9 |
73 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 3 |
79,3 |
84,9 |
|
85,8 |
86 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 4 |
|
107 |
|
111 |
113 |
112 |
|
|
|
|
| 5 |
|
128 |
|
134 |
138 |
138 |
137 |
137 |
137 |
|
| 8 |
|
177 |
|
194 |
207 |
214 |
|
|
|
|
| 10 |
|
|
|
|
248 |
263 |
266 |
267 |
267 |
|
| 12 |
|
|
|
|
286 |
309 |
|
|
|
|
| 14 |
|
|
|
|
320 |
353 |
|
|
|
|
| 16 |
|
|
|
|
352 |
394 |
|
|
|
|
| 18 |
|
|
|
|
|
452 |
|
|
|
|
| 20 |
|
|
|
|
|
495 |
504 |
511 |
511 |
|
| 25 |
|
|
|
|
|
558 |
613 |
628 |
632 |
|
| 30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
744 |
741 |
746 |
|
| 35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
812 |
848 |
860 |
|
| 40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
902 |
950 |
972 |
|
| 50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1070 |
1140 |
1180 |
|
| 60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1210 |
1320 |
1380 |
|
| 70 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1490 |
1560 |
|
| 80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1640 |
1730 |
|
| 90 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1900 |
|
| 100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2050 |
|
|
| Copyright
1998, Jim Lux / spherev.htm / 8 March 1998 |
|
|
|
| Spark
Gap Correction Factors |
|
|
| Effects
of atmospheric conditions |
|
|
|
| V
= k* V0 |
|
|
|
| where
k is a function of the air density d |
|
|
|
| d
= p/760 * (293 / (273+T)) where p in Torr and T in degrees C |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| d |
0,7 |
0,75 |
0,8 |
0,85 |
0,9 |
0,95 |
1 |
1,05 |
1,1 |
1,15 |
|
| k |
0,72 |
0,77 |
0,82 |
0,86 |
0,91 |
0,95 |
1 |
1,05 |
1,09 |
1,12 |
|
| The
voltage increases with humidity varying some 2-3% over a normal atmospheric
range of 8-15 g/m3. |
|
|
|
|
| Irradiation |
|
|
|
|
| If
the gap is illuminated with UV or X-rays, it is more easily ionized. The
effect is more pronounced with smaller gaps, a 20% reduction |
|
| for short gaps of a few cm when irradiated.
For this reason, UV irradiation is specified for accurate breakdown voltage |
|
|
| Copyright
1998, Jim Lux / spherev.htm / 8 March 1998 |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|